
What is Cupping?
Cupping is an alternative medicine that was originally thought to release toxins from the body by suctioning impurities to the surface for easy elimination. Over the years, more research has been conducted and additional benefits are now proposed. These benefits are very appealing for those who are injured or suffering from a physical and/or emotional ailment.
How does Cupping work?
A CMPT therapist will use a silicone cup to create suction over a painful or restricted area on your body. Once the cup is in place, the therapist will either have you remain stationary, glide the cup in multiple directions or have you stretch while the cups are in place. Varying the technique will allow the therapist to target multiple tissue restrictions, and scar tissue, while improving the restricted motion.
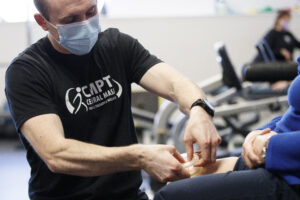
What are the benefits of Cupping?
Cupping has many reported benefits for both healthy patients and those suffering from an injury. Some of the benefits include:
- A quick, immediate reduction in pain, inflammation and swelling
- Increased blood flow and circulation to muscles
- Promotes relaxation and reduces tension in muscles
- Facilitates the healing process and strengthens the immune system
- Improvements in range of motion
What conditions would Cupping help with?
Cupping is one of the many manual therapies that we use with our patients. Any individual with swelling, pain, soft tissue restriction or loss of mobility may be appropriate for cupping therapy. Some other conditions include:
- Neck pain
- Lower back pain and/or tightness
- Headaches
- Upper trap tightness
- Scapular tightness
- Scar tissue
- Edema/swelling
Are there any side effects of Cupping?
Cupping is a very safe, non-invasive technique that carries little to no risk. Any side effect that does occur will typically present itself during, or immediately after, your treatment. The most common side effect that we see is redness in a circular pattern in the area where cupping was performed.